Calming Down is Hard To Do
Tantrums and meltdowns are high-stress moments for children and caregivers alike. As grown-ups, we want to help children process and control their strong emotions so moments like these occur less frequently.
But before we can start teaching self regulation — helping children manage their emotions and behaviors — we need to lay the groundwork. Remember: Young children just recently learned to walk, talk, and control their bladders. Jumping right to managing emotions can be a heavy lift!
Here are three important prerequisites that we should work on before helping children learn to control their emotions:
- Put Safety First
Before children are able to self-regulate, they need to feel safe both physically and emotionally. They need to know that their grown-ups support them and are going to listen to them and protect them. You help your child feel emotional security by sticking to a daily routine and by building time into your routine to listen and talk. Knowing that they have your attention gives children a sense of security. It also helps them feel safe to talk about feelings and gives you an opportunity to validate their thoughts and feelings. When you intentionally give affection and praise and even say the words “you are safe,” it helps children feel secure. It seems simple, but it’s powerful, especially after big emotions or moments of uncertainty.
- Build Connections
It’s important to build a positive relationship, rooted in trust, before attempting to teach children more advanced skills. You do this by being present and making eye contact; giving a high five or a hug; and playing! When you play together, let your child take the lead. Even 10 minutes a day can make a big difference. This Connected Families video: Spending Special Time With Your Child has more tips on building connections.
- Lead the Way
You’re a role model to the children in your life; they will mirror what they see YOU do. When they see you face frustrations and work through them in a positive way, they learn how to do it themselves. You don’t have to give a child a play-by-play of a frustrating work call, but you can talk to them, in age-appropriate ways, about how you feel and what you do about it. Having a meltdown from feeling strong emotions is expected from young children, and we can help them process their feelings by modeling self-awareness and showing them how to express feelings in healthy ways.
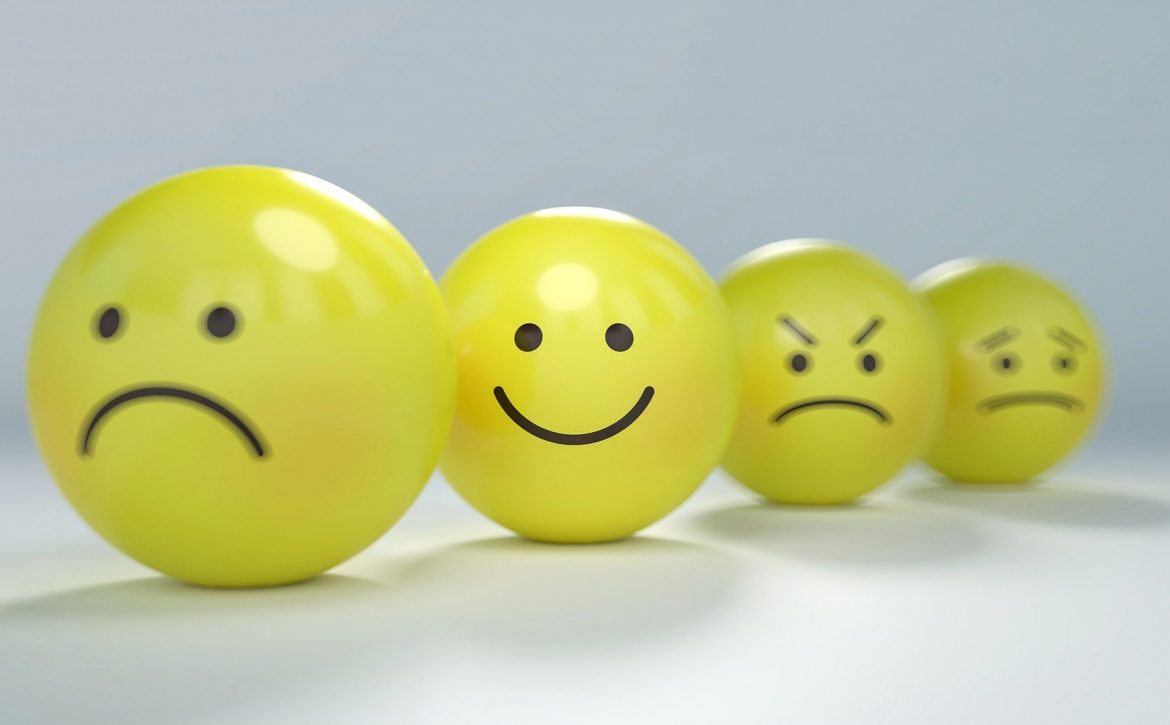
- Introduce the Feelings
Before a child can regulate emotions, they have to know how to identify those feelings with words — from happy to sad to angry. Talk about what our faces look like when we’re sad or what our bodies feel like when we’re mad. (This Connected Families video, Labeling and Acknowledging Emotions, will help learn more about the feelings.)
After you build trust, help your child feel safe, and guide them in understanding emotions, then you get to work with him or her learning to manage emotions — especially the BIG feelings that can lead to tantrums, meltdowns, and stress.